Isolation of muscle protein & depletion of acto-myosin components
From SDMRC
Contents
Isolation of muscle protein & depletion of acto-myosin components
Method Summary
This method describes how to isolate soluble muscle proteins (from heart or skeletal muscle), and prepare it for subsequent mass-spec analysis. Specifically, acto-myosin components are depleted from the sample to allow for mass-spec analysis of less abundant proteins.
Materials
Lysis buffer
- 300mM KCl
- 30mM PIPES pH6.6
- 0.5% NP-40
- 1x protease inhibitor (COMPLETE, EDTA free; Roche, Cat-No: 04693159001)
- 1x phos-stop (Roche, Cat-No.: 04906837001)
- 10mM Na-butyrate
Dilution buffer
- 1x Phos-stop (Roche, Cat-No.: 04906837001)
- 10mM Na-butyrate
- 0.5% NP-40
- 1mM DTT
Method
- Lyse hearts/muscle in ice-cold lysis buffer (approximately 500µl/30mg muscle; I used a polytron homogenizer)
- Centrifugate at max speed in a tabletop centrifuge (@ 4ºC) for 10 minutes & transfer supernatant into a new tube
- Dilute supernatant 1:4 with ice-cold dilution buffer (mix by inverting tube several times)
- Centrifugate at max speed in a tabletop centrifuge (@ 4ºC) for 15 minutes
- Transfer supernatant into a new tube & snap-freeze for mass-spec analysis.
- The pellet should contain the majority of the muscle acto-myosin and interacting proteins.
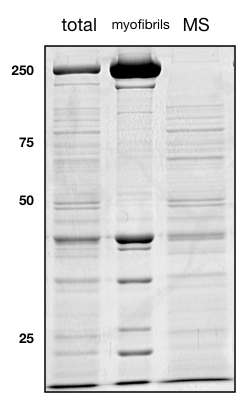
If everything worked out, a coomassie gel of the total samples (lane 1), the act-myosin myofibrillar components (lane 2) and the depleted supernatant mass-spec samples should look like the one here: